Print for your students:
High Flyers: 4 Helicopters & Airplanes
Book: Clorinda Takes Flight

Print a copy of the following for each student:
Print this list for yourself: Skills & Interests List
DISCUSSION:
Distribute the Skills & Interests Charts to the students and instruct them, as you read your list, to copy these items down on the appropriate side of their chart. Afterwards, discuss their charts and find aviation jobs that they would be likely to enjoy.

Print a copy for each student and one for yourself: Intro to Ground School: 8 Aviation Law
Be sure to have a copy of the FAR/AIM and, if possible, the FAR FC (Flight Crew) on hand so you can answer questions as they arise.

This is a big topic, so it will take two class periods to cover.
Print a copy of each of the following for each student:
And, if you are teaching a class, print the following for yourself: Meteorology Notes
DISCUSSION:
Quick intro: Weather on the ground vs. Weather in the air (flying)…
ATMOSPHERE
*** Diagrams***
WHAT CREATES WEATHER?
WHAT MAKES AIR MOVE?
WARM AIR (heated surface):
COOL AIR:
Think of oil and water:
** Moving air diagrams **
STABLE vs. UNSTABLE air
CLOUDS
ICING
THUNDERSTORMS
**PAGE 111! **
Print a copy for each student: Intro to Ground School: 5 Navigation
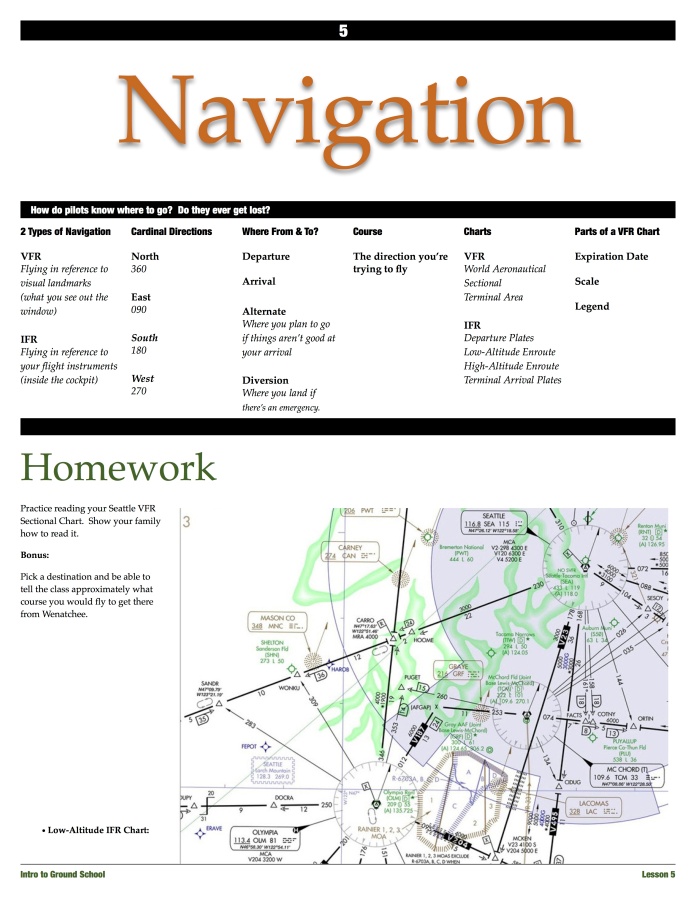
Unfold a copy of your local sectional chart and explain it to the students. Toward the end of class, show copies of low altitude and high altitude enroute charts, and a terminal area chart, for comparison.
At the end of the class period, distribute a copy of the sectional to each student for them to keep.
Print out enough copies of the following for each student to have one:
If you are teaching a class, print out a copy of the following for yourself: Flight Planning
DISCUSSION:

You can either write the above list, or ask the class for ideas and write those down, then add the things they have missed.
After your list is on the board, write the following list in a separate area:
Return to your original list and, after each item, ask the students which “planning category” covers that surprise. Write the abbreviation for that category after the surprise.
This exercise shows that most “surprises” can be accounted for in the flight planning process.


Print a copy for each student: Intro to Ground School: 3 Airports
DISCUSSION: (Airports)
Find in Google Earth: Kijabe Airport
Phases of Flight:
Cashmere Airport
Wenatchee Airport
Seattle Airport
Additional Resources:
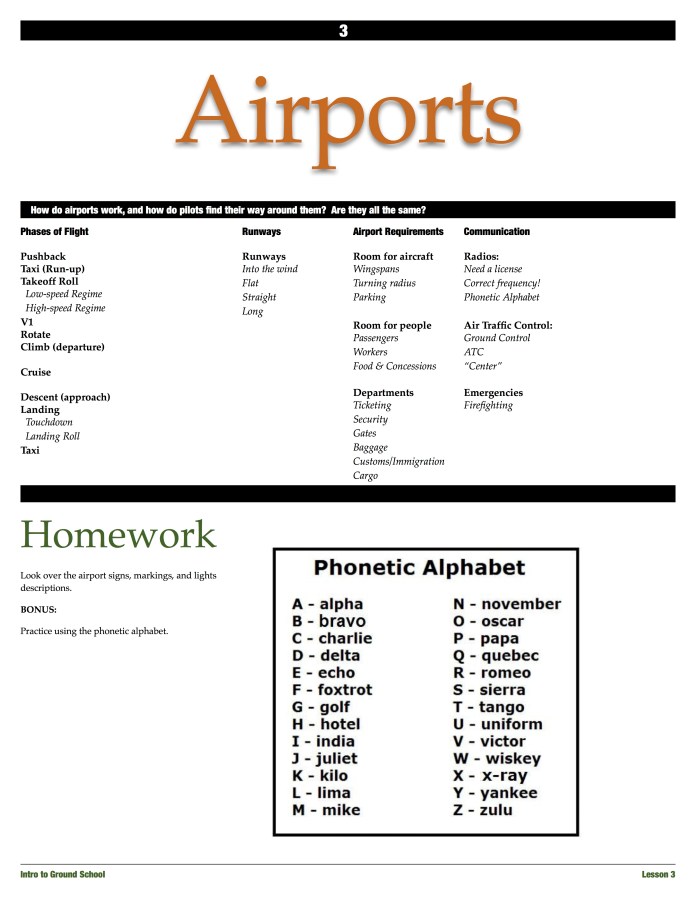
Taxiway Markings, Signs and Lights